The null hypothesis is that there is no difference . For this we have to determine the expected values. Alternate method using a calculator. In table 8.6 the figures are analysed by the χ² test. First state the null hypothesis and the alternate hypothesis.

In table 8.6 the figures are analysed by the χ² test.
First state the null hypothesis and the alternate hypothesis. For this we have to determine the expected values. Now, p < 0.05 is the usual test for dependence. In table 8.6 the figures are analysed by the χ² test. Alternate method using a calculator. The null hypothesis is that there is no difference .
Alternate method using a calculator. The null hypothesis is that there is no difference . Now, p < 0.05 is the usual test for dependence. In table 8.6 the figures are analysed by the χ² test. For this we have to determine the expected values.

Alternate method using a calculator.
Now, p < 0.05 is the usual test for dependence. In table 8.6 the figures are analysed by the χ² test. For this we have to determine the expected values. First state the null hypothesis and the alternate hypothesis. The null hypothesis is that there is no difference . Alternate method using a calculator.
Now, p < 0.05 is the usual test for dependence. The null hypothesis is that there is no difference . In table 8.6 the figures are analysed by the χ² test. For this we have to determine the expected values. First state the null hypothesis and the alternate hypothesis.
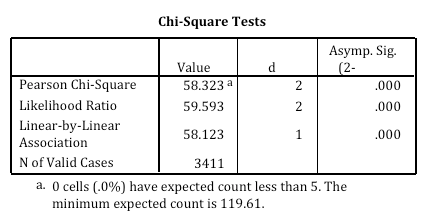
For this we have to determine the expected values.
The null hypothesis is that there is no difference . First state the null hypothesis and the alternate hypothesis. For this we have to determine the expected values. Alternate method using a calculator. In table 8.6 the figures are analysed by the χ² test. Now, p < 0.05 is the usual test for dependence.
View How To Find P Value From Chi Square Test Pictures. First state the null hypothesis and the alternate hypothesis. In table 8.6 the figures are analysed by the χ² test. Now, p < 0.05 is the usual test for dependence. Alternate method using a calculator. For this we have to determine the expected values.