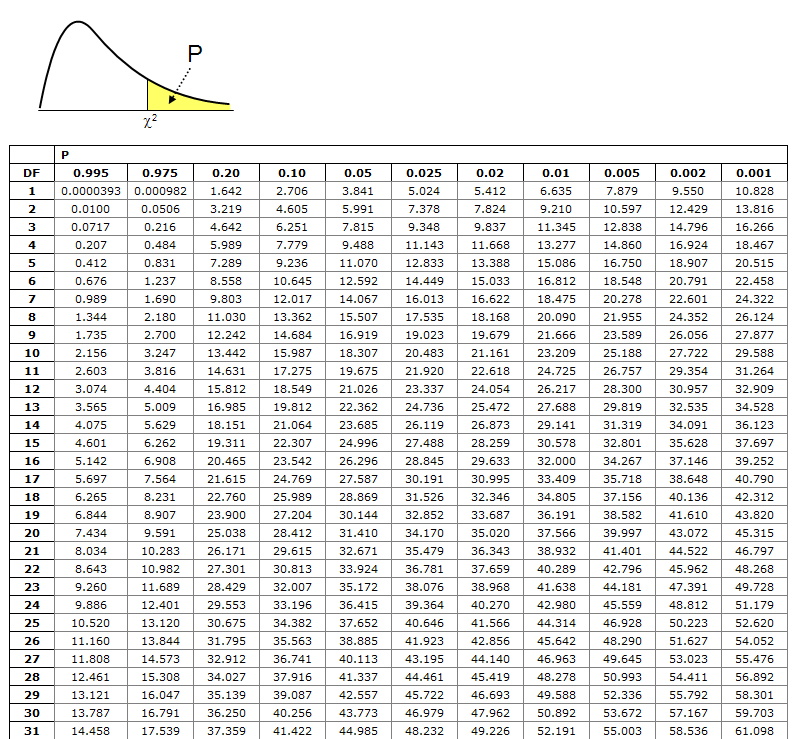
Statisticians calculate certain possibilities of occurrence (p values) for a x2 value depending on degrees of freedom . It helps you to decide whether to accept or reject the null hypothesis. The chi squared table below is used in hypothesis testing. The results are shown in table 8.2 , columns (2) and (3). Here i show one very simple version .

Statisticians calculate certain possibilities of occurrence (p values) for a x2 value depending on degrees of freedom .
Statisticians calculate certain possibilities of occurrence (p values) for a x2 value depending on degrees of freedom . Find the row that corresponds to the relevant degrees of . In a more general sense, it tests to see whether . It helps you to decide whether to accept or reject the null hypothesis. Having obtained a value for we look up in a table of χ² distribution the probability attached to it ( . A test statistic with ν degrees of freedom is computed from the data. The chi squared table below is used in hypothesis testing. Here i show one very simple version . The results are shown in table 8.2 , columns (2) and (3).
Having obtained a value for we look up in a table of χ² distribution the probability attached to it ( . Find the row that corresponds to the relevant degrees of . In a more general sense, it tests to see whether . A test statistic with ν degrees of freedom is computed from the data. The results are shown in table 8.2 , columns (2) and (3).
It helps you to decide whether to accept or reject the null hypothesis.
In a more general sense, it tests to see whether . The chi squared table below is used in hypothesis testing. Statisticians calculate certain possibilities of occurrence (p values) for a x2 value depending on degrees of freedom . Here i show one very simple version . Having obtained a value for we look up in a table of χ² distribution the probability attached to it ( . The results are shown in table 8.2 , columns (2) and (3). A test statistic with ν degrees of freedom is computed from the data. Find the row that corresponds to the relevant degrees of . It helps you to decide whether to accept or reject the null hypothesis.
It helps you to decide whether to accept or reject the null hypothesis. In a more general sense, it tests to see whether . Having obtained a value for we look up in a table of χ² distribution the probability attached to it ( . A test statistic with ν degrees of freedom is computed from the data. Find the row that corresponds to the relevant degrees of .

Having obtained a value for we look up in a table of χ² distribution the probability attached to it ( .
Statisticians calculate certain possibilities of occurrence (p values) for a x2 value depending on degrees of freedom . In a more general sense, it tests to see whether . A test statistic with ν degrees of freedom is computed from the data. Having obtained a value for we look up in a table of χ² distribution the probability attached to it ( . The results are shown in table 8.2 , columns (2) and (3). Find the row that corresponds to the relevant degrees of . The chi squared table below is used in hypothesis testing. Here i show one very simple version . It helps you to decide whether to accept or reject the null hypothesis.
16+ How To Use A Chi Square Distribution Table PNG. The results are shown in table 8.2 , columns (2) and (3). The chi squared table below is used in hypothesis testing. Statisticians calculate certain possibilities of occurrence (p values) for a x2 value depending on degrees of freedom . A test statistic with ν degrees of freedom is computed from the data. In a more general sense, it tests to see whether .